Details of the Project
Activities and Steps of the program
Activities of the program are summarized as the followings.
- Implement PHCI activities based upon proposals made by participatory planning in the levels of the community (village) and the sub-districts.
- Based on these experiences to implement such PHCI activities, develop "A Model of Participatory Primary Health Care Improvement (PHCI) Activities" that shall be an operational package of an institutional framework and capacity building for the district level health offices.
- Develop guidelines and manuals required for the above mentioned package.
Steps of PHCI Activities are summarized as follows.
- Form "PHCI Teams" both in the levels of the community and the sub-district. These teams will take initiatives to assess their PHCI needs and to prepare PHCI plans.
- Given their PHCI Plans, the PHCI Teams choose priority actions to be taken and propose what to do. They will also implement the proposed activities. The PHCI Teams, and thus the communities and sub-districts are the owners of the program.
- PHCI Teams will also review and report what they achieved or not achieved after they finish PHCI activities. The results of review will be used to make better plans and activities for the next year.
- The District Health Office will develop "A Model of Participatory Primary Health Care Improvement (PHCI) Activities" jointly with JICA Expert Team. A model should be designed to be applicable to other sub-districts.
Basic Approach
- Empowerment of the people
Empowerment of the people is the primary focus of the program. The real owners of the activities of PRIMA Kesehatan are the people in the community.
- The District Implementation Team - Core Actor of PRIMA
The District Implementation Teams are the core group of people to make PRIMA Kesehatan operational.
- Trainers: learning process for both trainers and participants.
- Facilitators: be creative to encourage and empower people.
- Monitoring and evaluation: do not be afraid of making mistakes. We can learn most from mistakes.
- Sustainable institutional arrangement - make the program stand by itself after 3 years.
"Learning By Doing Process"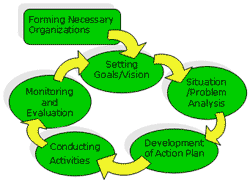 Figure 1: PRIMA - Cycle of PHCI Improvement
Figure 1: PRIMA - Cycle of PHCI ImprovementAs shown in Figure 1-1 below, PRIMA itself is the learning process. All the participants are going to experience planning, implementation, monitoring, evaluation, and re-planning through the activity cycle of PRIMA.
- Step by Step Expansion and Evolution
Operation of the program starts smaller in the first cycle (in 2007) of activities. In the second cycle, operation will be expanded to all target sub-districts. Each cycle has different focus.
- First cycle (2007-2008):
- The focus is put on capacity building of the District Implementation Team to become trainers and facilitators in order to empower PHCI teams in the levels of sub-district and community. Operation will be limited to two sub-districts in each district.
- Second cycle (2008-2009):
- The focus is put on expansion and generalization of PRIMA model within a district. Operation will be expanded to all selected sub-districts. The model shall be modified reflecting experiences in the first cycle.
- Third cycle (2009-2010):
- The focus is put on integration of all experiences in all three target districts to build a complete set of participatory PHCI model of PRIMA Kesehatan. Possible ways to apply PRIMA model to the other districts in South Sulawesi will be also explored.
