JICA values the relationship of mutual trust with developing countries and is working with them to rise to the challenges.
*Figures exclude JICA's cooperation for multiple countries and/or multiple regions and international organizations.
※Annual Report 2020:
Human Security:
Aiming for a society where all people can protect themselves from various threats and live their daily lives in security and with dignity.
Quality Growth:
Promoting sustainable growth with less disparity and without harming the environment.
A society where all can
live healthy, safe lives
- Education
- Health
- Social Security
A peaceful, just society without
fear or violence
- State-Building to Prevent the Outbreak and Recurrence of Conflicts
- Governance Support
- Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women and Girls
A prosperous, sustainable
economy at harmony with nature
and prepared for promoting
social development
- Agricultural and Rural Development
- Private Sector Development
- Urban and Regional Development
- Ensure Access to Affordable and Clean Energy
- Development of Transport Infrastructure
Care for the Planet
- Environmental Conservation and Management
- Water Resources Management
- Disaster Risk Reduction
- Climate Change
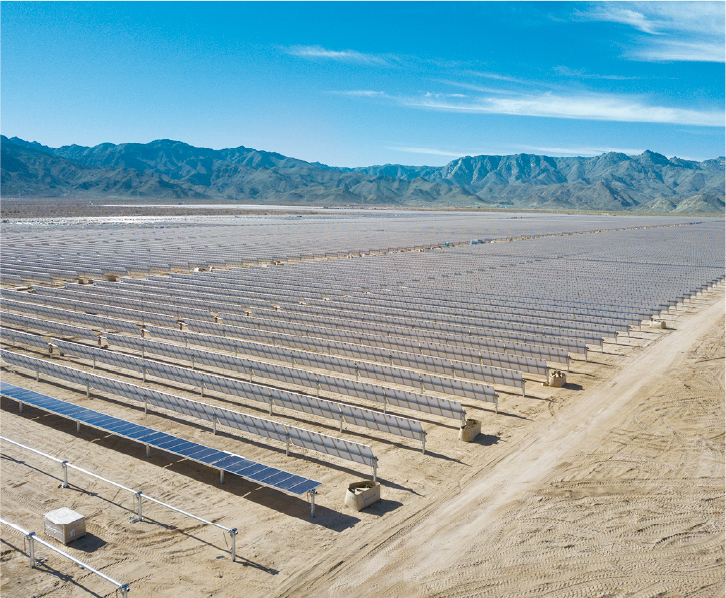

JICA signed a loan agreement with Infraestructura Energética Nova, S.A.B. de C.V. (IEnova), a Mexican energy company, for expanding its large-scale solar generation business and contributing to the efforts to combat climate change
(Mexico)
Photo courtesy of IEnova.
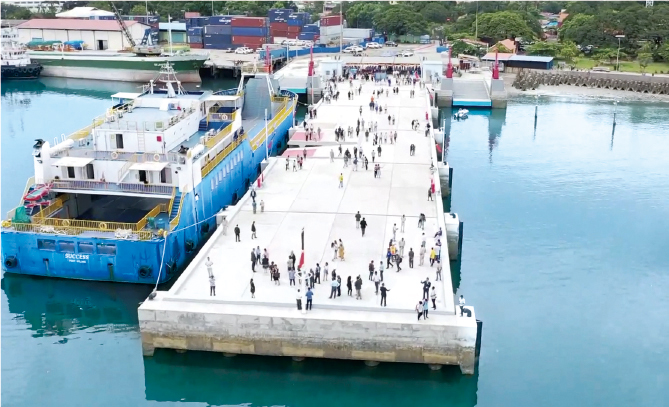

The Port of Dili, the country's only international port. The existing ferry terminal was relocated and expanded, contributing to the expansion of safe and efficient marine transportation
(Timor-Leste)
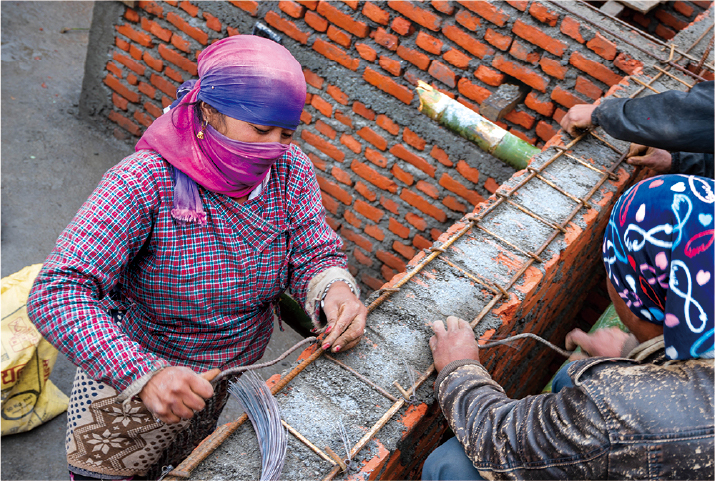

After the Nepal Earthquake of 2015, JICA contributed to rebuild homes under the concept of Build Back Better by promoting construction of quake-resistant buildings with local communities
(Nepal)
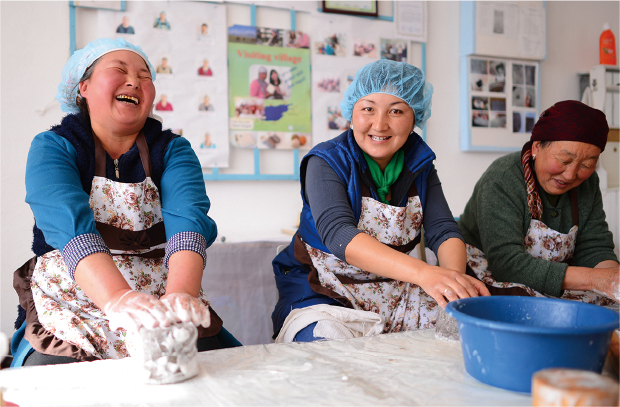

The One Village One Product (OVOP) project contributes to the revitalization of the local economy and to the empowerment of women
(Kyrgyzstan)

JICA cooperates in the development and O&M of the Delhi Metro utilizing Japanese technology and experience
(India)
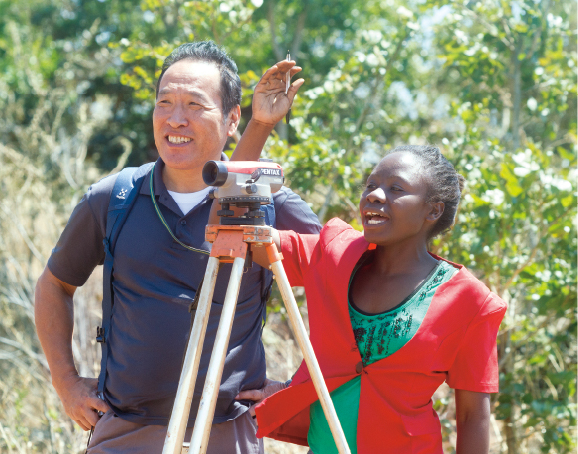

A Malawian irrigation engineer making a land survey under the supervision of a Japanese expert in the Project for Enhancing Capacity for Medium Scale Irrigation Scheme Development, Operation, and Maintenance
(Malawi)

In the Coalition for African Rice Development (CARD), JICA has contributed to increase rice production mainly in 23 CARD member countries through assistance in disseminating rice cultivation techniques, an area in which Japan has an advantage
(Tanzania)
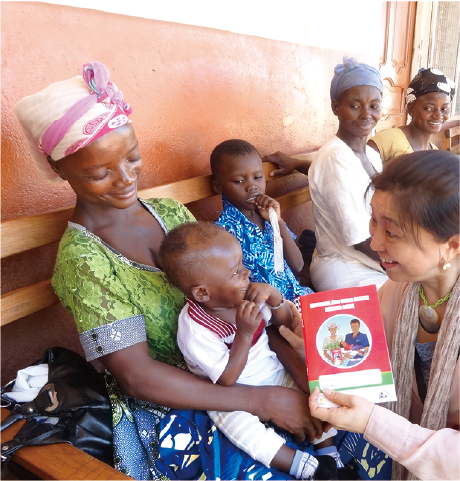
JICA cooperates to introduce and institutionalize the Maternal and Child Health (MCH) Handbooks for mothers and children to protect their lives and health. More than 9 million copies of the MCH Handbooks were issued in 34 partner countries in 2019 alone
(according to a JICA estimate)

Japan Overseas Cooperation Volunteers (JOCV) involved in activities at a football academy to improve the coaching skills of instructors
(Cambodia)

JICA contribute to the training of female police officers who support women survivors of gender-based violence
(Afghanistan)
JICA dispatches experts and overseas volunteers to developing countries, and in return welcomes government officials and specialists as training participants and overseas students. People-to-people connections established through human resource development are the foundations of trust between developing countries and Japan.
JICA uses an array of development assistance schemes to meet the diverse needs of developing countries around the world
Technical Cooperation(*1)
Dispatch of Japanese experts to developing countries and acceptance of training participants and students to disseminate Japanese technologies and knowledge
2. Public works and utilities 22.6%
3. Agriculture, forestry and fisheries 10.6%
4. Mining and industry 1.4%
5. Energy 3.0%
6. Business and tourism 3.0%
7. Human resources 11.2%
8. Health and medical care 5.9%
9. Social welfare 1.3%
10. Others 32.9%
Finance and Investment Cooperation (ODA Loans)(*2)
Lending or investing of funds under concessional terms to developing countries for their development
2. Transportation 36.0%
3. Agriculture, forestry and fisheries 4.1%
4. Social services 22.5%
5. Program loans 2.4%
6. Others 2.7%
Grants(*3)
Financial assistance with no repayment obligation; it mainly targets developing countries with low levels of income.
2. Public works and utilities 51.0%
3. Agriculture, forestry and fisheries 6.7%
4. Energy 5.1%
5. Business and tourism 0.8%
6. Human resources 14.9%
7. Health and medical care 17.5%
8. Others 1.5%
(Note) In some cases, the numbers do not correspond to the figures reflected in the “Total” section because of rounding estimates. *1 Technical Cooperation expenses include Technical Assistance expenses managed under the Finance and Investment Account budget, but exclude administration costs. *2 Total commitment amounts of ODA Loans and Private-Sector Investment Finance. *3 The amount is calculated based on the fiscal 2019 budget, it does not correspond to the total amount of Grant Agreements (G/As) concluded in fiscal 2019. ※ Total value of JICA programs in the map do not include cooperation track records that cannot be categorized by region.
JICA's volunteer programs
Citizen Participation
Partnership with Nikkei Communities
in Latin America and the Caribbean
Emergency Disaster Relief
Studies and Research
Public-Private Partnerships







