Outline of the Project
Project Name
Health Systems Strengthening for HIV and AIDS Services Project
Terms of Cooperation
Oct. 26, 2010 to Oct. 25, 2014
Target Area
The United Republic of Tanzania
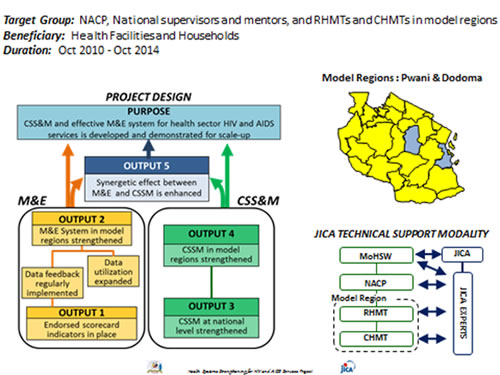
(Model regions: Pwani and Dodoma)
Target Group
National AIDS Control Programme
National supervisors and mentors
Regional Health Management Teams (RHMTs) and Council Health Management Teams (CHMTs) in Dodoma and Pwani Regions
Beneficiaries
RHMTs, CHMTs, Health Facilities and Households
Background of the Project
In the United Republic of Tanzania, hereinafter referred to as Tanzania, AIDS epidemic has grown as a national emergency and great threat to the development of the country since the advent of the epidemic in 1983, despite efforts which had been recorded in a great number of interventions to control the disease starting with prevention intervention to care and treatment. However, constraints in human resources and weaknesses in health systems have been the key bottlenecks for the expansion of the interventions and delivery of quality services. Successful scale-up and utilization of broad range of HIV and AIDS related services requires a well-functioning health system.
One of the weaknesses identified in the current health systems is Monitoring and Evaluation (M & E) System. Strengthening M & E is one of the top priority areas of Ministry of Health and Social Welfare (MOHSW) as stipulated in the Health Sector Strategic Plan III (HSSP) (2009-2015). Due to the cross-cutting nature of M & E, the National AIDS Control Programme (NACP) through the Health Sector HIV Strategic Plan II (HSHSP II) has been striving to establish comprehensive M & E system for the health sector response to HIV and AIDS.
Another weakness is on ensuring quality of HIV and AIDS services. In 2010, MOHSW through NACP developed three important documents: the National Essential Health Sector HIV and AIDS Interventions Package, National Guidelines for Quality Improvement of HIV and AIDS Services and the Manual and Tools for Comprehensive Supportive Supervision and Mentoring for HIV and AIDS Health Services. All these documents needed to be operationalized in the health delivery system and the desired health outcomes need to be pursued.
The Health Systems Strengthening for HIV and AIDS Services Project, hereinafter referred to as the Project, began its operation in October 2010 with duration of four years. The Project is focusing on enhancement of M & E and comprehensive supportive supervision and mentoring for HIV and AIDS services.
Framework of the Project
Activities under Output 1 focus on central-level data management of HIV and AIDS services. A set of essential indictors were selected and set by NACP as the HIV/AIDS Scorecard Indicators which enable NACP to track and visualize present situation of HIV/AIDS services in regional comparison.
Output 2 focuses on strengthening data feedback and utilization at regional and council levels in the model regions. Activities include installation of the IT equipment, data analysis training, development of data feedback system and on-the-job training on data analysis. The scorecard indicators were introduced as an entry point to help the RHMTs and the CHMTs in the model regions to get familiar with data analysis, visualization and interpretation. The activities have induced practical utilization of the routinely collected data in the field, which have been recognized as good practices and presented in national and international conferences.
Output 3 laid the base of a Comprehensive Supportive Supervision and Mentoring (CSS&M) at the national level through the development of training curriculum and materials for CSS&M, implementation of trainings for national and regional supervisors and mentors. The training has been conducted in the model regions as well as other regions in collaboration with implementing partners. The actual implementation of CSS started from the national to the regional level. Based on the needs identified, mentors have been also dispatched to meet the technical/clinical needs. The Project also developed an archive system for CSS&M which promotes information sharing and utilization for improvement of HIV and AIDS services.
Output 4 is set to strengthen the CSS&M in the model regions as part of quality improvement of HIV and AIDS services, aiming to create a model of CSS&M. The focus of Output 4 is to strengthen the managerial foundation of CSS&M among RHMTs and CHMTs in the mode regions in a sustainable manner. A number of CSS&M trainings were conducted in the model regions to facilitate the full execution of the CSS&M. Assessment of CSS&M implementation was conducted in the model regions and the findings were shared among the stakeholders for their actions to improve their CSS&M.
Output 5 is focusing on a synergy effect between M&E and CSS&M. The data feedback materials with routinely collected data from the health facilities have triggered natural integration of data feedback and supportive supervision.
- About JICA
- News & Features
- Countries & Regions
- Our Work
- Thematic Issues
- Types of Assistance
- Partnerships with Other Development Partners
- Climate Change / Environmental and Social Considerations
- Evaluations
- Compliance and Anti-corruption
- Science and Technology Cooperation on Global Issues
- Research
- JICA Development Studies Program / JICA Chair
- Support for the Acceptance of Foreign HRs / Multicultural and Inclusive Community
- Publications
- Investor Relations
