Overview by Region
Latin America and the Caribbean
Aiming to Further Co-creation by Deepening Partnerships
Overview by Region
Latin America and the Caribbean
Aiming to Further Co-creation by Deepening Partnerships
Common development issues in the region and emerging needs
Latin America and the Caribbean comprises 33 countries with a total population of 650 million*1 and a total GDP of over $5.4 trillion,*2 about 1.8 times the size of ASEAN.*3 These countries are diverse, ranging from Mexico and Brazil, both of which are large in area and exporters of food and mineral resources, to Costa Rica, a small country that leads the world in the area of environmental initiatives, and to Caribbean countries, where tourism is a major industry. Yet many of them share a common language and culture.
Countries in the region share with Japan universal values such as freedom and democracy. Being home to more than 2.13 million Japanese emigrants and their descendants (Nikkei) in total,*4 these countries have historically close relations with Japan as well. Geographically, they are Japan’s neighbors across the Pacific. They are also Japan’s important partners in addressing common challenges such as frequent natural disasters.
Many countries in the region are prone to natural disasters such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and hurricanes, and are faced with public security issues and irregular migration. Although the region generally enjoys high income levels, it faces widening economic disparities among and within the countries. Responding to an aging population, introducing digital transformation (DX), and building a start-up ecosystem also constitute some of the emerging development needs in the region.
Taking on development issues together with diverse stakeholders
JICA’s cooperation for this region focuses on stable and resilient socioeconomic development and the creation of an environment that is more conducive to economic development through trade and investment. It also focuses on addressing global challenges such as disaster risk reduction and climate action. Additional focus is placed on cultivating leaders with knowledge of Japan and strengthening relations with Nikkei communities in the region.
The total committed amount of Finance and Investment Cooperation for the region in fiscal 2022 was the largest ever. This covered, among other projects, an urban transport network development project in Panama and a financial inclusion project for Costa Rica. JICA also continued to work on common regional issues in cooperation with development partners in the region, including the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Pacific Alliance (Mexico, Colombia, Peru, and Chile). In addition, JICA provided cooperation regarding mobility and logistics in Central America in collaboration with the Central American Integration System (SICA) and also promoted south-south and triangular cooperation with Brazil and Mexico.
Moreover, JICA agreed with the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) to work together to alleviate the root cause of irregular migration in Guatemala. JICA’s collaboration with the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB) involves development cooperation in the sectors of quality infrastructure, disaster resilience, and health through co-financing schemes, as well as the TSUBASA Program, which supports innovative Japanese start-ups in doing business in the region to solve development issues there. Supported under the program, some Japanese firms have already made inroads into the region. In fiscal 2022, an additional 11 companies were selected to receive such acceleration support.
*1 World Bank Group, “DataBank
Microdata Data Catalog,” 2021.
*2–3 International Monetary Fund, “World
Economic Outlook Database,” 2022.
*4 Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan,
“Nikkei people connect Japan with Latin
America and the Caribbean,” a brochure
in Japanese only.
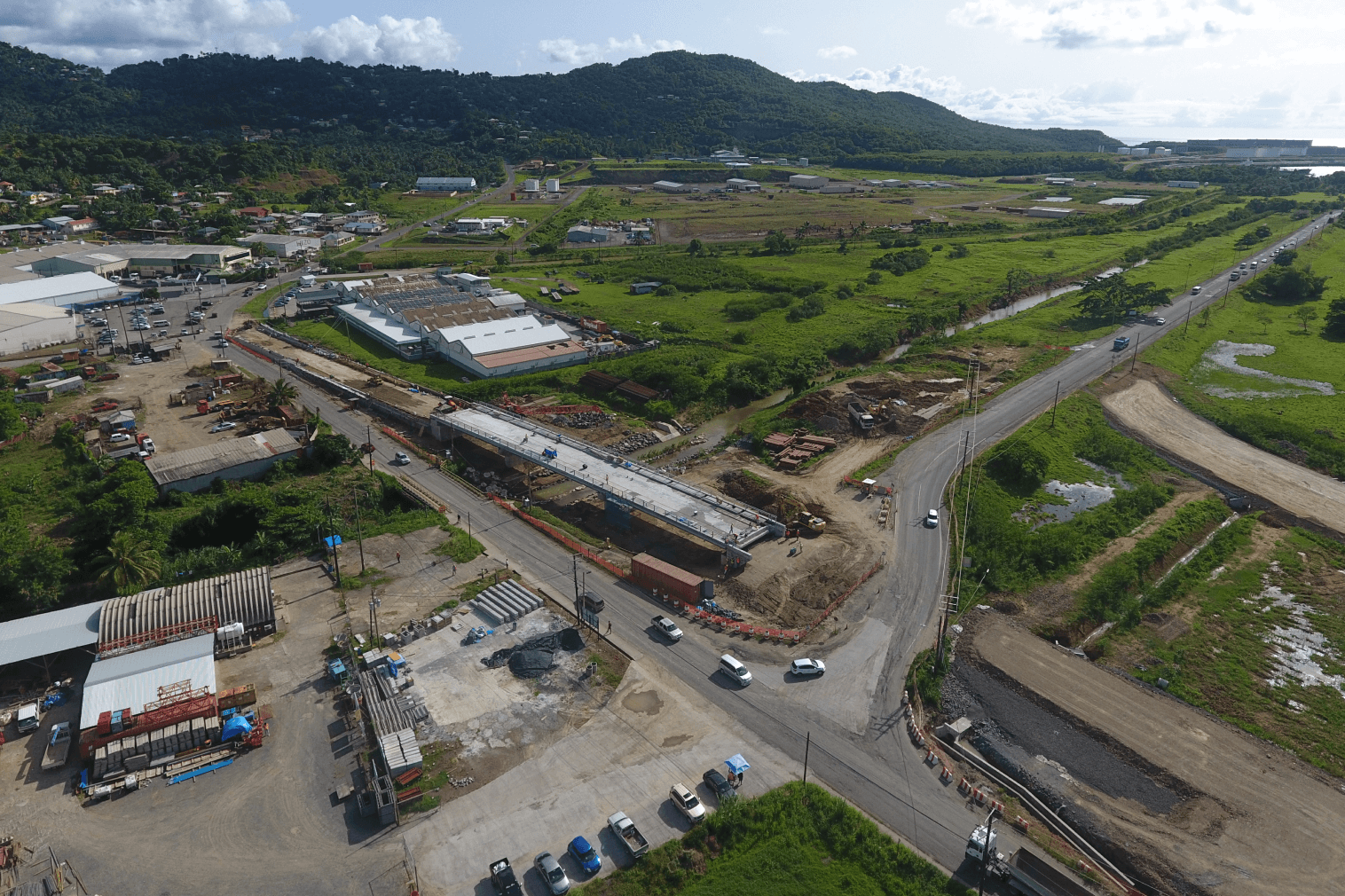
Saint Lucia: The country’s frequent experience with natural disasters makes it urgent to develop transportation infrastructure that supports both evacuation in times of disaster and post-disaster reconstruction efforts. JICA cooperated in the reconstruction of Cul de Sac Bridge, which connects the capital city and the international airport.
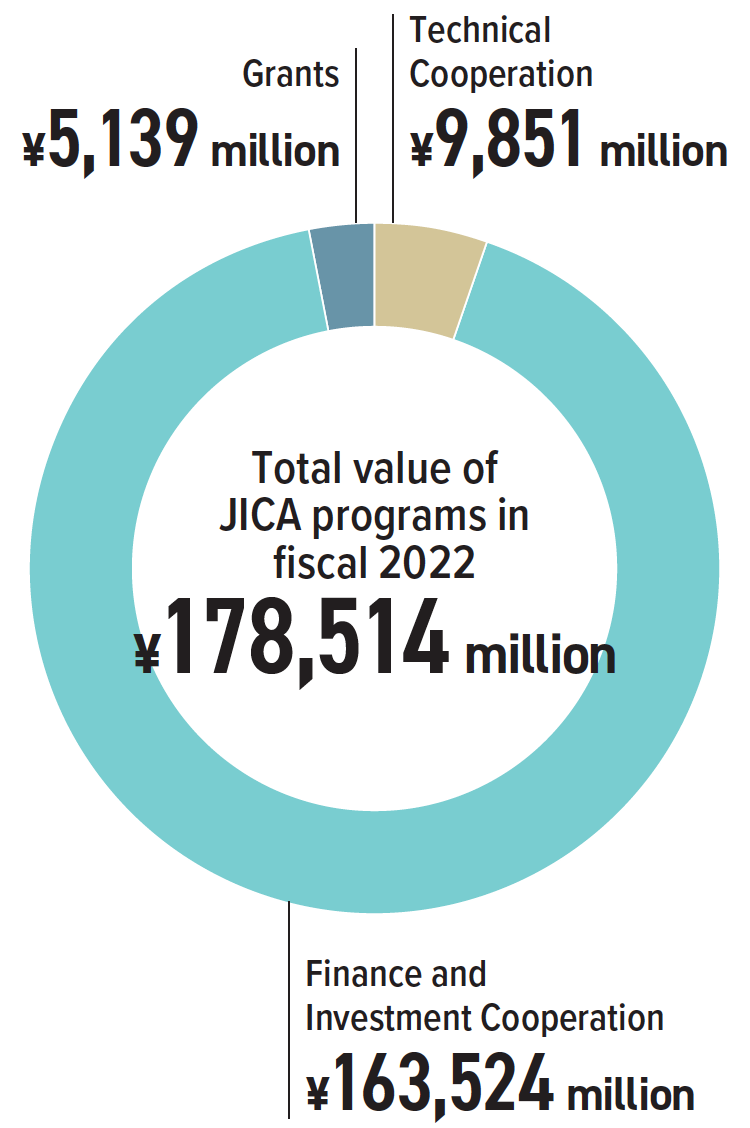
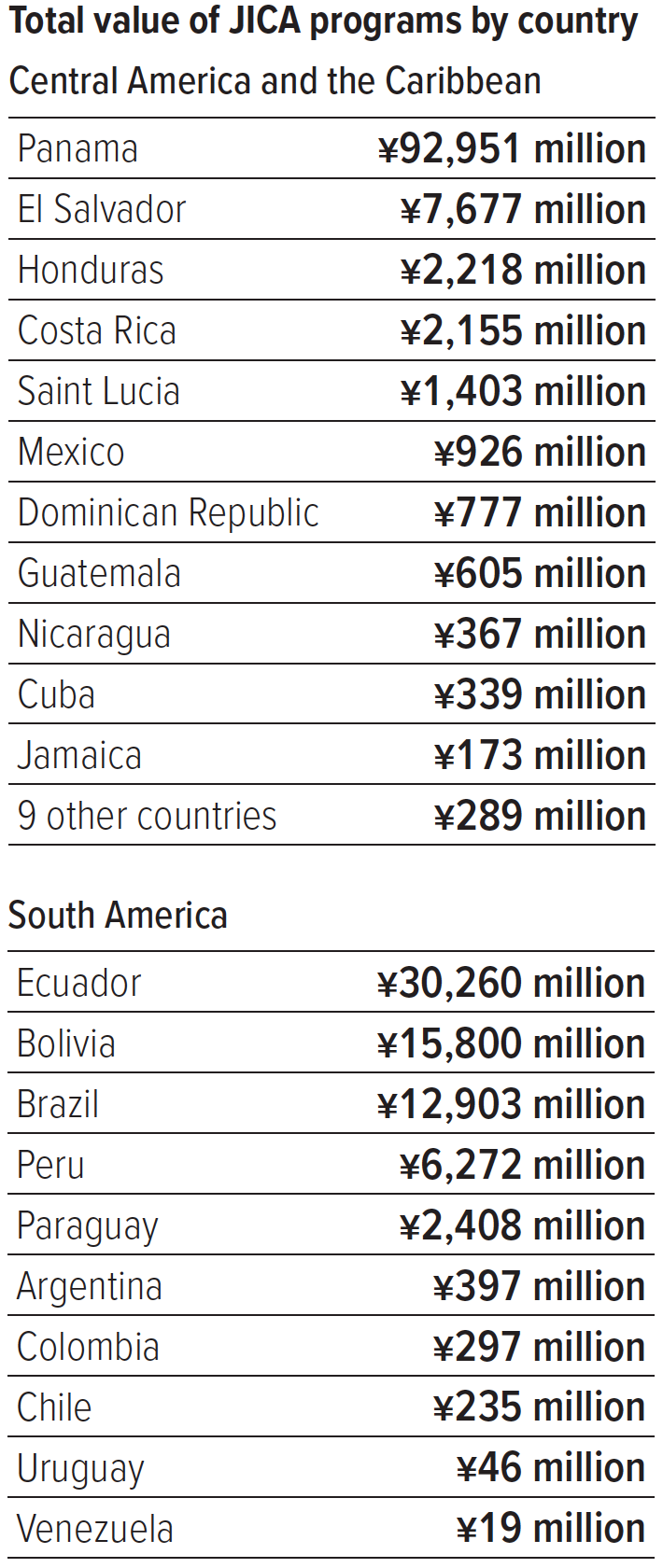
Note: For the total value of JICA programs, see the note on “Programs by Region” on page 37. For Central America and the Caribbean, the above table lists only countries with program value of ¥100 million and over. Totals may not add up due to rounding.

