Overview by Region
Africa
Working on TICAD 8 Initiatives toward a Resilient, Inclusive, and Prosperous Africa
Overview by Region
Africa
Working on TICAD 8 Initiatives toward a Resilient, Inclusive, and Prosperous Africa
Compounded crises and TICAD 8
Africa is faced with compounded crises that involve deepening climate change and socioeconomic difficulties resulting from the pandemic and the Ukrainian situation, such as food crises and deteriorating debt sustainability. In a dynamic global community, African countries, which account for one-quarter of the United Nations membership, are increasing their presence as an emerging political and economic power.
In August 2022, representatives of 48 African countries gathered in the Tunisian capital of Tunis to join the Eighth Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD 8). At TICAD 8, the Japanese government announced that Japan, as a partner growing together with Africa, will support the realization of a resilient Africa that Africa itself aims to achieve through a virtuous cycle of growth and distribution.
Contributions to fulfill Japan’s commitments
To implement the initiatives Japan announced at TICAD 8, JICA is enhancing efforts to achieve the following objectives as part of its cooperation aimed at addressing compounded crises and exploiting Africa’s potential.
1. Food security
In November 2022, JICA announced its Africa Food Security Initiative, which aims to achieve human security through food and agriculture development. Under the initiative, JICA is engaged in (1) food production,(2) fostering of farmers and agribusiness, (3) nutrition improvement, and (4) climate action . At TICAD 8, JICA announced an agricultural cooperation package totaling $300 million in cooperation with the African Development Bank (AfDB). As the first tranche, JICA signed a loan agreement totaling ¥15 billion with Côte d’Ivoire.
2. Promotion of business that solves social issues
To ramp up support for innovative start-up businesses that work to solve social issues in Africa, JICA helps build a start-up ecosystem at the national level under Project NINJA (Next Innovation with Japan), as well as supports local health care businesses in cooperation with the African Union Development Agency (AUDA-NEPAD). In addition, JICA has decided to invest in a venture capital fund under its program of Private-Sector Investment and Finance.
3. Promotion of regional economic integration
JICA signed a memorandum of cooperation (MOC) with the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) Secretariat to support the implementation of the AfCFTA agreement toward Africa’s economic integration. Based on this MOC, JICA will step up efforts to develop a regional infrastructure network, facilitate trade, and build intraregional value chains, among others.
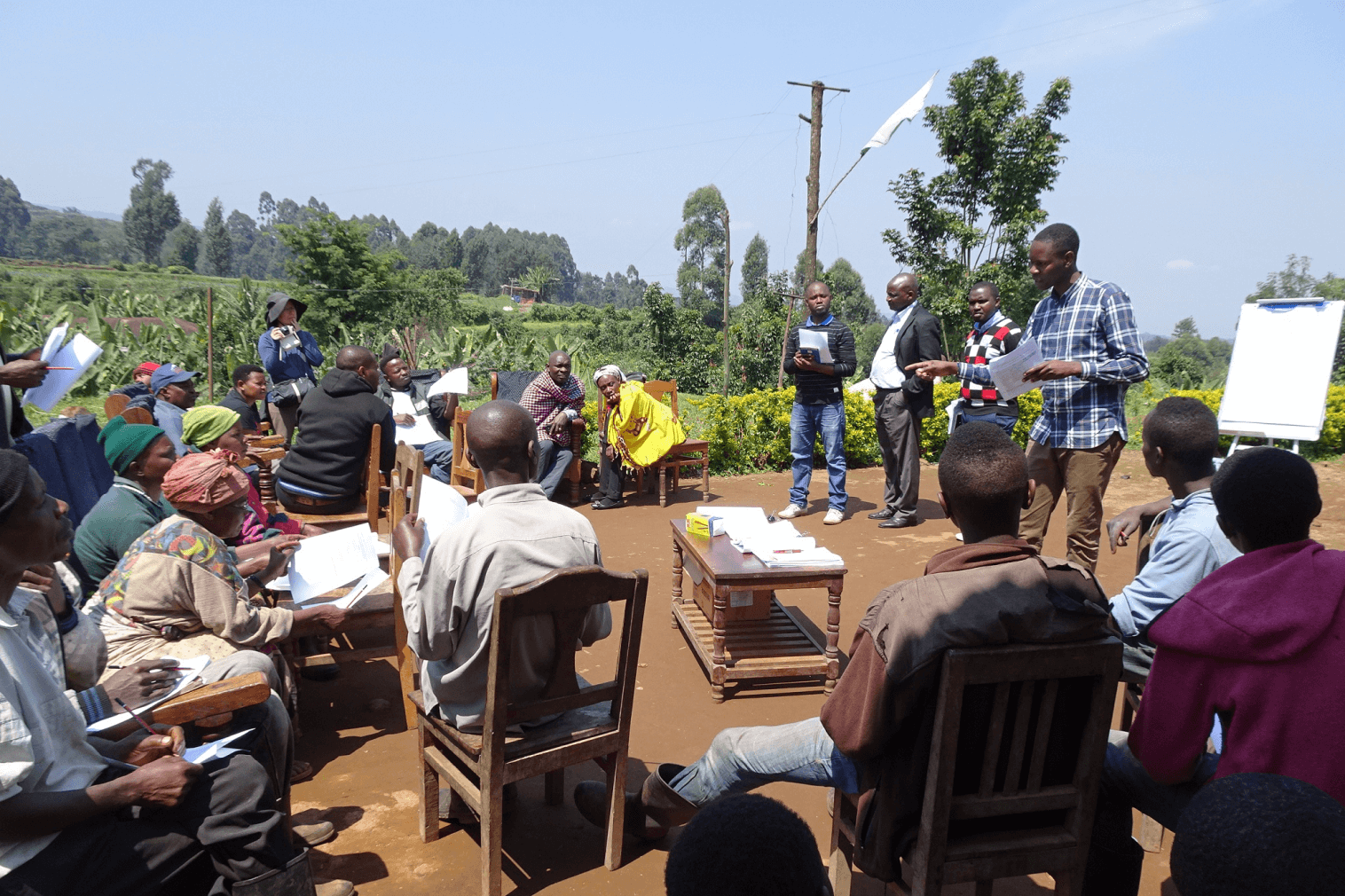

Tanzania: A group of farmers planning market research as part of an initiative undertaken through the Smallholder Horticulture Empowerment and Promotion (SHEP) approach. This initiative is aimed at increasing horticulture income through a planting and marketing approach addressing market needs.
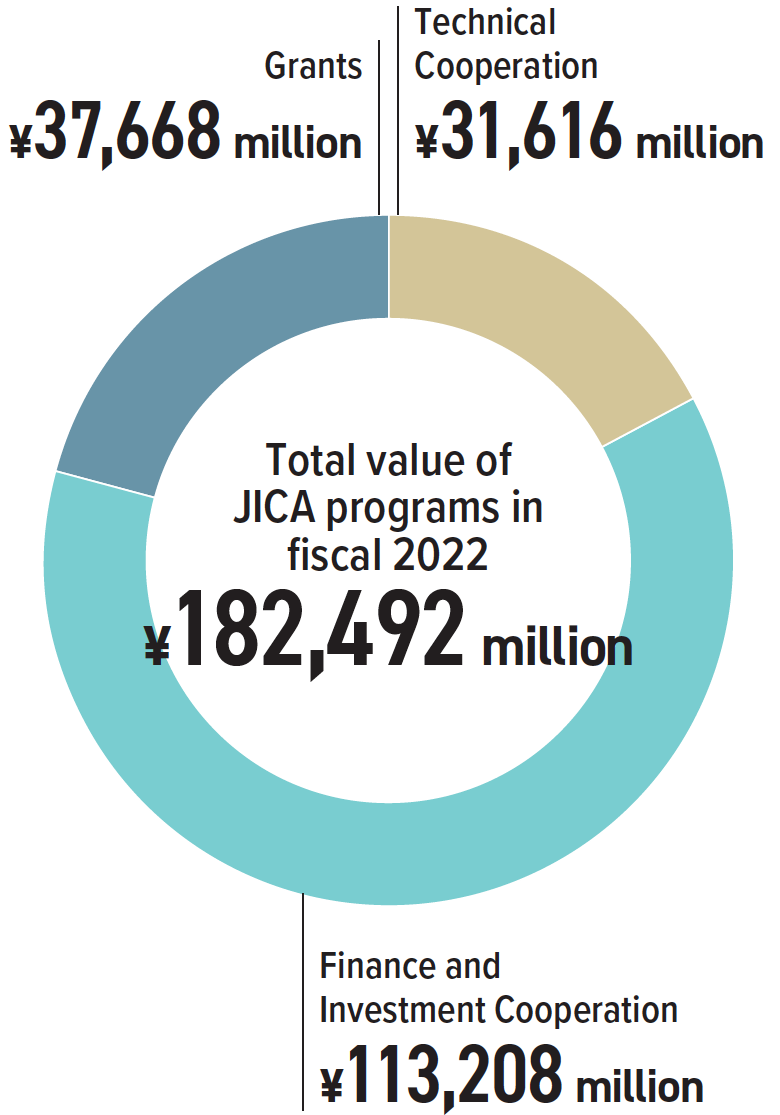
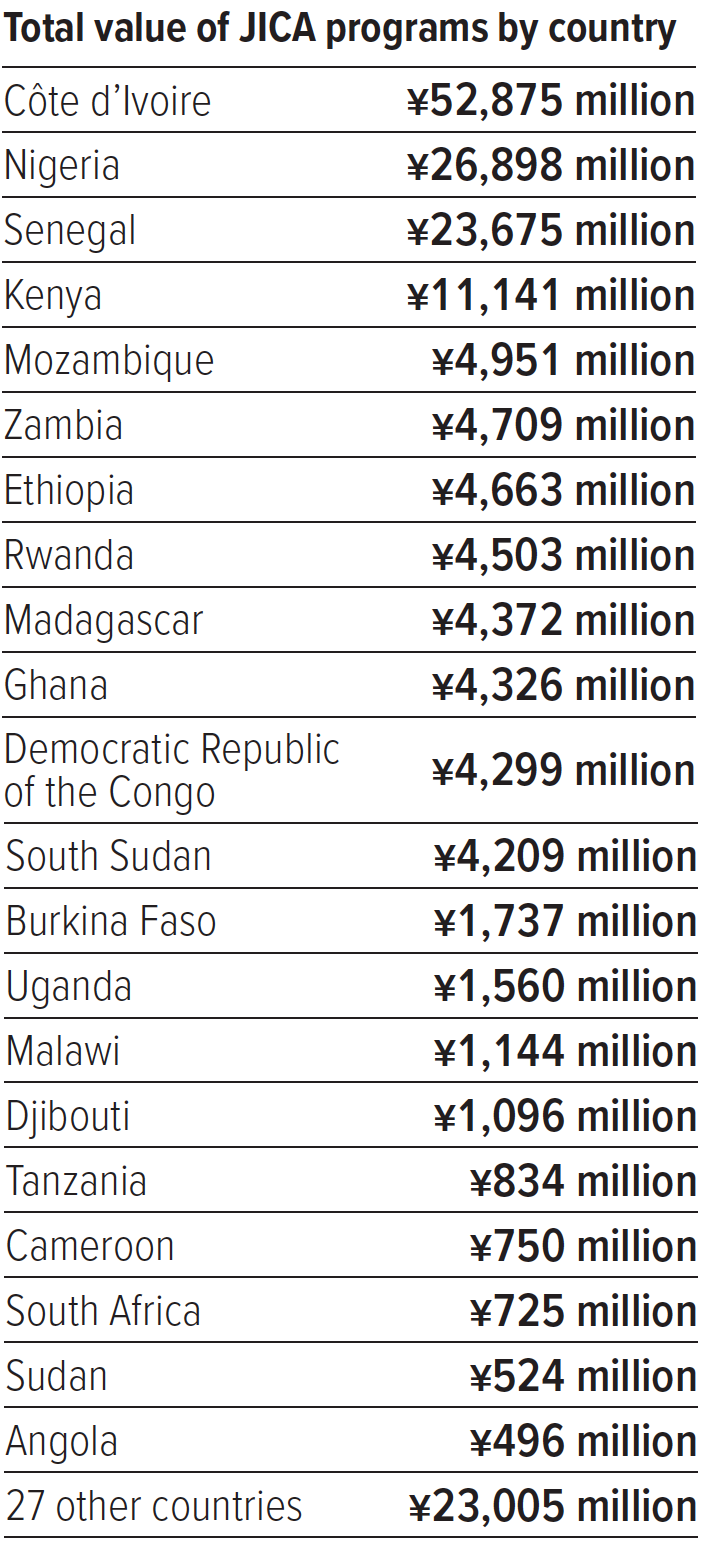
Note: The table lists only countries where JICA’s overseas offices in Sub-Saharan Africa are located. For the total value of JICA programs, see the note on “Programs by Region” on page 37. Totals may not add up due to rounding.

