Background and Objective
Although Tunisia is a small country with a total land area of 164 thousand square kilometers—about 40 percent the size of Japan—the annual rainfall differs greatly depending on the region. While the north of the country has a mild Mediterranean climate, the south is a semiarid desert, making it critical for Tunisia to develop a water management system capable of using the north’s abundant rainfall to supply the entire country.
The actions had been taken in the past to develop water resources, which were interrupted by massive flood of the Medjerda River in January 2003. This river originates in the Atlas Mountains of eastern Algeria, crossing Tunisia’s northern region to the Mediterranean at Tunis Bay. The flood submerged the downstream alluvial plains near the capital city of Tunis for more than a month, disrupting transportation and causing widespread damage to crops and homes that affected the region socially and economically.
The development study of integrated water resource development and management was therefore dedicated to devising a master plan that incorporated environmental protection measures for the Medjerda River Basin. Medjerda River is the largest river in all Tunisia, and it is required to have an effective prevention of flood and sediment-related disasters.
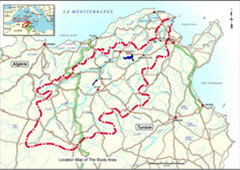
Target region

Seventeenth-century bridges on the Medjerda River
Cooperation Summary
Planning based on on-site surveys:
JICA study teams were dispatched to Tunisia multiple times from November 2006 to December 2008 for its on-site surveys. Working together with engineers from Tunisia’s Ministry of Agriculture and Water Resources, JICA carefully implemented the study of the condition of river basin, simulation analyses, some meetings to discuss the engineering requirements of the plan and exchanged opinions with local inhabitants.
The final output is a comprehensive master plan for flood control on the Medjerda River that consists of “structural” and “non-structural” measures to prevent flood disaster.

On-site survey with Tunisian engineers

Tunisian engineers receive
technical training in Japan
Results of the simulation of flood disaster in Medjerda River:
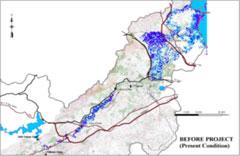
Current conditions.
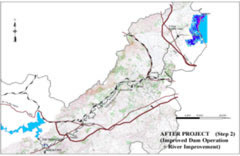
After the improvement of Dam
operation and river improvement
proposed in the master plan.
Master Plan Proposal Summary
-
1
.
Structural-measure of flood prevention
Efficient usage of reservoirs and implementation of river improvement to protect municipalities along the Medjerda River -
2
.
Non-structural-measure of flood prevention
Improvement of flood warning system, enhancement of evacuation and flood control procedures to minimize the damage from excessive flood.





scroll