Sector Overview
Tanzania’s industries, which consist mainly of labor-intensive ones, require diversification and sophistication. High unemployment and an immature startup (SU) ecosystem are also issues to be addressed.
According to TDV2050, the share of the manufacturing and service industries in GDP is on the rise. More than 60% of the population is still engaged in labor-intensive industries such as agriculture, and sufficient employment opportunities are not created. The diversification and sophistication of industries is becoming an issue to be addressed. In addition, to promote domestic and foreign investments, it is essential to ensure transparency and improve the business environment. Moreover, although the potential labor force is plentiful with approximately 43% of the population under 15 years of age and approximately 65% under 25 years of age, the high unemployment rate, particularly among young people, and the mismatch with the human resource needs of the industry are issues to be addressed.
SMEs (Small and Medium Enterprises) play an important role in the economy, accounting for approximately 35% of GDP and 70% of the working population in 2022. However, challenges include weak financial inclusion, insufficient information on business laws and regulations, and access to capital.
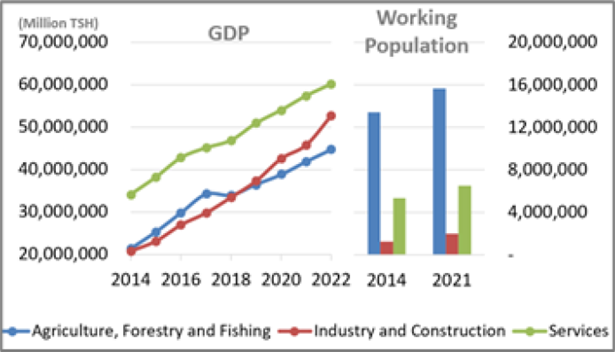
GDP and working population by sector (2014-2021)
(Source: Ministry of Finance and the National Bureau of Statistics)
In addition, although SUs is becoming increasingly important as they receive valuable employment in the country, there are capital shortages and regulatory and policy issues, which point to the immaturity of the ecosystem. Securing skilled human resources, supporting SUs, and bringing technological innovation are also necessary for the growth of the manufacturing and service industries. In particular, the utilization of ICT and the development of the digital industry are issues to be addressed in the future.
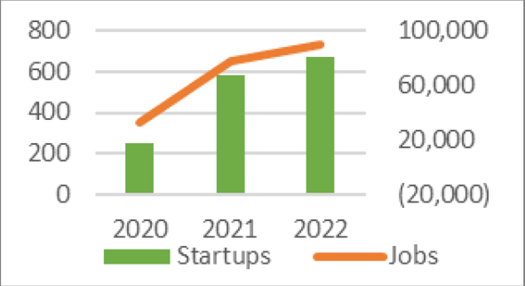
SUs and Employment by SUs
(Source: Tanzania Startup Association)





scroll