Outline of the Project
Project Name
The Project for Rural Water Supply, Sanitation and Livelihood Improvement through Dissemination of Rope Pump (RPs) for Drinking Water (WAS-RoPSS: ዉሃን በጥረቴ)
Implementation Organization
Water Supply and Sanitation Directorate, Ministry of Water, Irrigation and Electricity (MoWIE), Water and Irrigation Development Bureau of SNNPR
Target Area
4 woredas in SNNPR
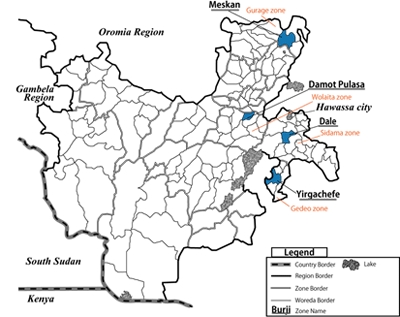 Project Map (Main)
Project Map (Main)
 (Sub)
(Sub)
Project Period
March 2013 – December2016
Project Background
In the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, hereinafter referred to as ‘Ethiopia', the proportion of the population who has access to safe water is only 44%, while the average for Sub-Saharan African countries is 61%. The government of Ethiopia set the target of water supply coverage of 98.5% by 2015 in the Universal Access Plan 2 (UAP2) which is a five-year development plan of the water and sanitation sector. In particular, this plan focuses on the rural water supply, with the average increment of the coverage rate being about 7% annually.
Japan, as a long-term development partner of Ethiopia, has provided financial and technical assistances in rural water supply sub-sector for the last several decades, as shown by reports such as, "Eleven Centres Water Supply and Sanitation", "Project for Water Supply in Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples' Regional State", and "The Project for Water Supply in Afar Region". In addition, several technical cooperation projects, such as Ethiopia Water Technology Centre Project (EWTEC) and the Water Sector Capacity Development Project in Southern Nations, Nationalities and People's Regional State in the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia (WAS-CAP) have contributed to human and organizational capacity development, as well as technical extension. These two projects also contributed to the new sphere of rural water supply technology, rope pumps, herein after referred to as ‘RP'. RP, as a low cost water-lifting device which can be self supplied by the rural people, was improved and introduced by these projects.
RP is now increasingly valued as one of the low cost technologies for ‘self supply' since the government has placed it in its national guidelines and plans. However, dissemination of RPs has until now been limited for several reasons. For instance, some untrained local manufacturers forged RPs, which were so low in quality that they malfunctioned. These low quality RPs in turn contributed to RP's bad reputation and lowered the market values of RPs in some areas. The absence of the appropriate financial support system to the rural people also contributed to the slow expansion of the RP market. It is therefore essential that the government has clear national strategies for accelerating the dissemination of RPs, which may include the financial support system for the rural people, as well as improvement of RPs as a valued market commodity.
The government of Ethiopia requested technical assistance from Japan in August 2010, and JICA conducted the Detailed Project Planning Study in March-April 2012 and June 2012. As a result, it was found that the government of Ethiopia has already made good progress in the acceleration of self-supply. Consequently, the technical assistance shall not be limited only to improvement and standardization of RPs but shall be extended to dissemination and marketing of RPs. Both parties agreed the project design and signed the Record of Discussion in August 2012.
Objectives
Overall Goal
Water supply and sanitation condition and livelihood in rural areas are improved through dissemination of RPs for Drinking Water in Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples Region.
Project Purpose
Situation of water supply, sanitation and livelihood are improved through dissemination of RPs for Drinking Water in project target areas.
Outputs
- Specifications of RPs for drinking water and installation technologies are standardized at the federal level.
- Strategies are formulated for manufacturing, installation technologies, operation and maintenance of RPs for drinking water.
- Promotion activities on RP including hygiene education are accelerated by the governmental and semi-governmental organization in the target woredas.
- Practices of RP use including hygiene are supported continuously by the village technicians and extension workers in the target areas.
- Project knowledge and experiences are compiled as dissemination tools and acknowledged in SNNP and other Regions.
Main Activities
- Improvement and standardization of rope pump technology
- Formulation of strategies for RP quality control; operation and maintenance
- Supporting human resource development in RP technology through TVET system
- Introduction of certification of RP technology through COC system
- Dissemination of RPs for multi-purpose use (drinking and livelihood improvement)
- Promotion of hygiene and sanitation including household water treatment and storage (HWTS)
- Introduction of microfinance for Self-supply
- Preparation of technical manuals, guidelines, handbook and tools for RP promotion
- Working in harmony with partner organisations for Self-supply promotion; Self-supply group, private sector service providers and governmental and non-governmental organisations
- About JICA
- News & Features
- Countries & Regions
- Our Work
- Thematic Issues
- Types of Assistance
- Partnerships with Other Development Partners
- Climate Change / Environmental and Social Considerations
- Evaluations
- Compliance and Anti-corruption
- Science and Technology Cooperation on Global Issues
- Research
- JICA Development Studies Program / JICA Chair
- Support for the Acceptance of Foreign HRs / Multicultural and Inclusive Community
- Publications
- Investor Relations
