Outline of the Project
Project Name
Project on Small and Medium Industry (SMI) Development Based on Improved Service Delivery
Country
Indonesia
Project Site
Jakarta, Central Java Province, Central Sulawesi Province, North Sumatra Province
Date of Agreement
Dec.07, 2012
Implementing Organization
Directorate General of Small and Medium Industry (DG of SMI), Ministry of Industry (MoI) and local governments of target regions (especially Industry and Trade Offices)
Project Background
Indonesia has been implementing the 5-year "National Mid-term Development Plan" (the current one is for the period 2010-2014), based on the "National Long-term Development Plan (2005-2025)" as a fundamental policy for development. MoI, as the responsible ministry for industrial development, formulated the "Strategic Plan (2010-2014)" for promoting industrial cluster and local industrial development in line with the "Presidential Regulation No.28, 2008 on the National Industrial Policy" issued in May 2008 as a guideline for industrial policy including SMI development.
MoI determined a basic policy for industrial development consisting of the following 2 pillars: i) the ‘Top-down Approach (priority industry cluster development)', where MoI selects prospective industries and leads the planning and implementation of the action plan, and ii) the ‘Bottom-up Approach (priority industry/ core-competence development)', through which provincial and district/ city governments identify local resources, and formulate and implement the action plan for enhancing value addition to the resources and its commercialization.
Under the said policy and programs, JICA undertook a master plan study titled "Strengthening of Cluster (SENTRA) of Small and Medium Industries (2009-2010)" upon request from the Government of Indonesia. The study recommended, for effective SMI (cluster) development, i) establishment of an SMI development system not only in the central government but also at the regional level in a proper way, ii) dissemination of the concept on cluster development, and iii) placement of practical facilitators. Availability of support service for SMI development was also presented in the study; central/ regional governments and other service providers hold various support activity/ service for SMIs, including the placement of Shindan-shi.
On the other hand, the following issues are identified: Support activity/ service are generally planned and implemented according to considerations and procedures of the providers' side, SMIs as beneficiaries of supports do not recognize what and when such support activity/ service are available, resulting in inflexibility in their provision according to the needs of SMIs. That is to say, supports to SMIs have problems in their delivery. The demand from SMIs is growing, requiring that appropriate support activity/ service which respond to their needs are discussed with, prepared and provided by the relevant service providers. Hence, improvement and enhancement of such "service delivery mechanism (referred to as service delivery platform later on)" is considered urgent.
In this situation, the Government of Indonesia requested the Government of Japan to provide a technical cooperation project with MoI to establish an efficient service delivery platform and prepare for the socialization of the model to other regions.
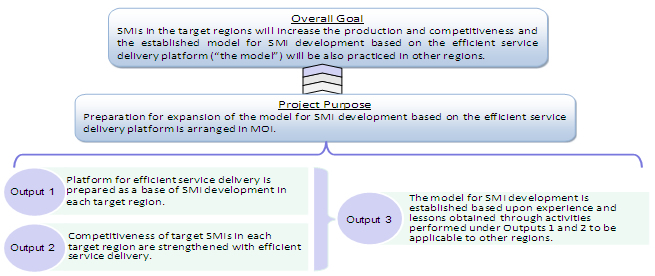
Overall Goal
SMIs in the target regions will increase the production and competitiveness and the established model for SMI development based on the efficient service delivery platform1 ("the model") will be also practiced in other regions.
Project Purpose
Preparation for expansion of the model for SMI development based on the efficient service delivery platform is arranged in MOI.
Outputs
- Platform for efficient service delivery is prepared as a base of SMI development in each target region.
- Competitiveness of target SMIs in each target region is strengthened with efficient service delivery.
- The model for SMI development is established based upon experience and lessons obtained through activities performed under Outputs 1 and 2 to be applicable to other regions.
Activities
| 1-1 | Set up the project implementation unit organized by DG of SMI in MoI for overall management of the Project. |
| 1-2 | In each target region, formulate Local Working Group (LWG) to coordinate the activities for SMI development for overall management of the Project. |
| 1-3 | Review and map the currently available institutions and services for SMI development by various entities and service providers2 in each target region. |
| 1-4 | Establish the system to ensure efficient service delivery for SMIs. |
| 1-5 | Assign and train staff in charge at the local government who facilitate services3 by local and central governmental institutions and private service providers for SMIs (attention shall be paid for the Shindan-shi). |
| 1-6 | Develop a Service Directory to introduce SMI support services by government and private institutions. |
| 1-7 | Facilitate and support activities of LWGs in each target region. |
| 1-8 | Monitor situation of service delivery in each target region. |
| 2-1 | Conduct regular meetings of LWGs in each target region. |
| 2-2 | Analyze issue and needs of value chain and industrial linkage in target SMIs in each target region (considering the target SMI’s type such as local resource-based industry and supporting industry). |
| 2-3 | Identify the goals, tasks, and activities for the development of the target SMIs based on the result of the analysis done above. |
| 2-4 | Implement the identified activities by using improved service delivery mechanism. |
| 2-5 | Analyze and evaluate the result of activities for development of target SMIs by LWGs in each region. |
| 3-1 | Analyze and evaluate the experience which is acquired through Activities under Outputs 1 and 2 in each region. |
| 3-2 | Identify contents and factors to constitute the model, which is adaptable to other regions. |
| 3-3 | Develop the guideline as reference materials for other regions to replicate and implement the model. |
| 3-4 | Organize workshop to socialize the model for other stakeholders. |
| 3-4 | Facilitate the necessary budgetary arrangement as well as formulate program to respond to the possible requests from other provincial governments out of target areas. |
In brief, the The Project aims to facilitate product development or improvement and its marketing promotion by target industries (SMIs) in 3 Project sites (target regions), through improving and strengthening the system to discuss, prepare and provide support activity/ service efficiently for SMI development (service delivery platform). Furthermore, such a SMI development through service delivery platform will be established as "work model" for other regions, based on the lessons learned from experiences in target industry and region.
| 1: Service delivery platform (or mechanism) | System which provides efficient support activity/ service for SMI development. In the Project, this shall be established in each target region/ industry aiming to discuss, prepare and provide support activity/ service based on needs of SMIs, and consist of LWG made of local service providers including government institutions related to target industry, facilitator, information on available support activity/ service in region and guideline for local industrial development. |
|---|---|
| 2: Service provider | Organization and/ or individual that provides support activity/ service contributing to business development. Governments and other public support institutions are also included. The content of support activity/ service covers managemant support such as business planning/ financial access as well as technical support, for instance, processing technology/ quality control. Service providers are also called as business development providers (BDS). |
| 3: Facilitator | Person who mediates and facilitates utilization of support activity/ service by SMIs. The Project assigns a wider role for facilitator, analysing issues/ needs of the target industry, facilitating discussion/ planning/ implementation/ monitoring & evaluation of action plans, assisting service providers who deliver respective support activity/ service (planning, budgeting, implementation), to complement the role of LWG. |
Target industries
The following industries are suggested by MoI and local governments of the Project site (one from each region according to the regional jurisdiction of DG of SMI) as the target of the Project, i.e., the service delivery platform to be improved and strengthened through the Project:
Region I: Ulos fashion industry (in Samosir District in North Sumatra Province)
Region II: Metal parts industry (in Tegal District in Central Java Province)
Region III: Cacao processing and rattan furniture industries (in Central Sulawesi Province)
Counterparts and beneficiaries
Counterparts (C/Ps) of the Project are DG of SMI as a core member, other related directorate general of MoI and related ministries, the Indonesian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (KADIN) and the Bank Indonesia (BI) at the central level. Meanwhile, at the regional level, provincial and district/ city governments (especially Industry and Trade Office) in the Project site, the Regional Chambers of Commerce and Industry (KADINDA), branch offices of BI, universities and other related service providers are also included.
Those C/Ps both in MoI and the Project site are the direct beneficiaries of the Project, who shall establish and continuously operate the service delivery platform as the output of the Project. Furthermore, SMIs in the target regions/ industries are considered as the indirect beneficiaries.
Inputs
Indonesian side:
- Appropriate number of C/P personnel in MoI
- Office space and facilities for the project
- Local cost necessary for C/Ps in the project activities
Japanese side:
- Experts (Chief Advisor, Local Industry Development, Supporting Industry Development, Financial Access, SMI Service Delivery, Project Coordinator)
- C/P training in Japan
- Provision of equipment necessary for the project activities
- Local cost for the project activities
- About JICA
- News & Features
- Countries & Regions
- Our Work
- Thematic Issues
- Types of Assistance
- Partnerships with Other Development Partners
- Climate Change / Environmental and Social Considerations
- Evaluations
- Compliance and Anti-corruption
- Science and Technology Cooperation on Global Issues
- Research
- JICA Development Studies Program / JICA Chair
- Support for the Acceptance of Foreign HRs / Multicultural and Inclusive Community
- Publications
- Investor Relations
