Dr. Yoichi Haga
Technology
Development of minimally invasive medical and healthcare devices leveraging micro- and nanomachining technologies
Integration of microfabrication technologies such as micromachining, nanotechnology, and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems)
Strength
Enabling low-burden examinations and treatments for patients using endoscopes and catheters, as well as the development and training of safe treatment methods
Use Case
①
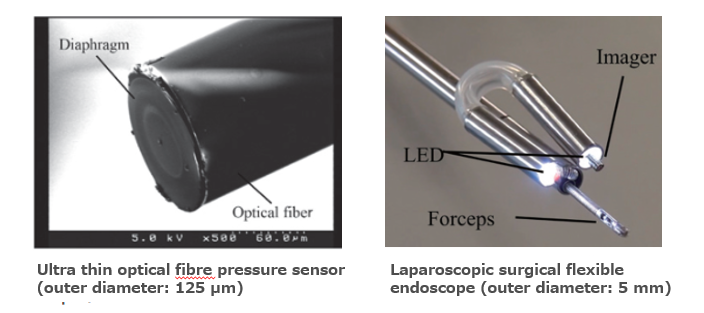
Development of small, high-performance, multi-functional, minimally invasive medical devices such as endoscopes, catheters, and surgical instruments
By inserting thin medical devices like endoscopes and catheters into the body without large incisions, it is possible to perform examinations and treatments comparable to conventional surgeries
②
Development of organ models with built-in sensors for precise measurement of effects on the human body
Organ models designed for verifying the effectiveness of medical devices and for surgical training. Equipped with microsensors capable of precisely measuring pressure changes and tissue deformation, these models enable accurate simulation of impacts on the human body
Dr. Makoto Ohta
Technology
Technology for measuring and simulating blood flow conditions through computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis
Strength
Enables the quantitative evaluation and simulation of the effects of drugs, medical devices, and procedures targeting blood vessels.
Contributes to the development of therapeutic drugs and medical devices as well as the improvement of surgical techniques for physicians
Use Case
①
Measurement of the effects of therapeutic drugs and medical devices on blood flow in blood vessels
The development of new therapeutic drugs and devices requires an objective evaluation process to assess their performance and safety. This technology particularly contributes to the development of therapeutic products targeting blood flow
②
Development of organ models with mechanical properties similar to blood vessels
Organ models designed for verifying the effectiveness of medical devices and for surgical training. These models, created using 3D printing and other techniques, replicate the physical properties of human blood vessels, bones, and other organs, enabling the engineering (numerical) evaluation of surgical techniques and medical device characteristics
Business Model Examples
This section shows examples of companies using this technology for its businesses. The sections is intened for illustrating how the technology is used in the real world as food for thoughs for the applicants. Applicants doesn't necessarily follow the exact business model when developing their own business ideas.
Blue Practice Inc
Business Contents
Development of Bionic Humanoids: Sophisticated Medical Models with Built-In Sensors
The vascular model incorporates sensors capable of detecting internal pressure, wall stress, and shape changes of blood vessels at micro-level precision. This data is then visualized numerically for detailed analysis
Social Issues
Until now, Doctors have had no choice but to learn catheter insertion through observation, leading to variations in individual skill levels
Solution
By training with a vascular model and simultaneously quantifying the conditions inside the vessel, it becomes possible to objectively identify areas for improvement, such as where the catheter gets stuck and how to insert it more effectively
Value
This approach enhances doctors' training motivation and contributes to further skill development for veteran physicians
Message from the Lab
What We Want to Know

Graduate school of Biomedical Engineering, Tohoku University
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Professor
Prof. Yoichi Haga, M.D., Ph.D.

Tohoku University, Institute of Fluid Science, Professor
Prof. Makoto Ohta
The demand for vascular models and the background situation in hospitals, medical device manufacturers, and evaluation agencies across various countries
Desired Candidate Profile
- Students interested in or experienced in business related to medicine and pharmaceuticals
- Medical students who intend to work at or have experience working in university hospitals




scroll